FAQ
- M051 Base Series(95)
- M0518 Series(97)
- M0519 Series(43)
- M0564 Series(1)
- Mini51 Base Series(90)
- Nano100/102 Base Series(101)
- Nano103 Base Series(10)
- Nano110/112 LCD Series(100)
- Nano120 USB Series(111)
- Nano130 Advanced Series(110)
- NUC029 Series(94)
- NUC100/200 Advanced Series(102)
- NUC120/122/123/220 USB Series(116)
- NUC121/125 Series(1)
- NUC126 USB Series(2)
- NUC130/230 CAN Series(103)
- NUC131/NUC1311 CAN Series(98)
- NUC140/240 Connectivity Series(114)
Products
Applications
Function
+
FAQ
How to calculate the necessary HXT accuracy(ppm) for a full speed USB device? Issue Date:2018-03-07
There is an accuracy parameter (ppm) for any external crystals, for example 12M+/-100ppm, and there are independent clock source from full speed USB device and hos. USB SPEC. has defined a frame timer range to be 500ppm.
Below is USB2.0 Spec. definition about frame timer range in ppm.
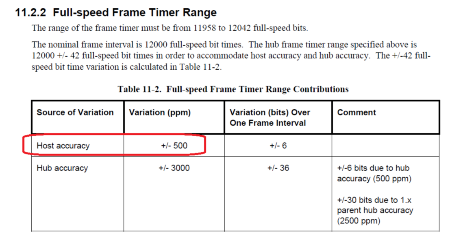
Nuvoton has no constrain of the crystal accuracy and user can calculate the effect to USB by the following calculation. (PFM-M487 has HXT with +/-30ppm)
There are two major errors contribute to USB clock, one is the crystal accuracy and the other is PLL jitter.
- Crystal ppm contribution – For a 100ppm crystal pass through the PLL to the USB clock has still 100ppm at the end of USB clock.
- PLL Jitter contribution – By datasheet, the maximum PLL jitter is 250ps (RMS, Figure1). PLL Jitter (192MHz) pass to USB (12M) has a divider of 16 timers and 250ps jitter will become 250ps/16 = 15.625ps (RMS) at USB clock. Transform RMS jitter to peak-to-peak period jitter by equation1 of Figure2, 7.44*15.625 = 116.25ps. For a full speed USB, it takes 1 ms for a single frame and jitter ppm calculation will be 116.26ps/1ms=116.25ppm
- The final USB in ppm = 100ppm(by crystal) + 116.25ppm(by PLL jitter) = 226.25pps still less than 500ppm. By this calculation, we can make sure that a crystal with 100ppm is fine for a full speed USB devuce.
Figure1:
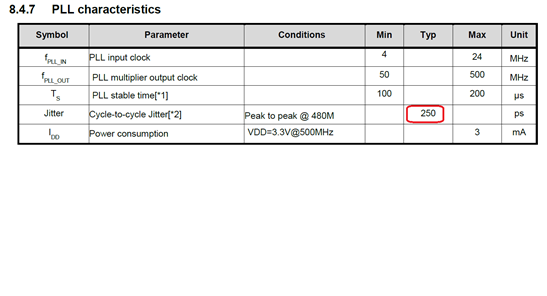
Figure2:

| Products: | |
|---|---|
| Applications: | |
| Function: | Peripherals,Clock Control,HXT,PLL,Connectivity,SPI,USB |